E-INVOICE IN GST
APPLY ONLINE FOR E-INVOICE IN GST
E-invoice in GST refers to the generation of a standard electronic invoice by a taxpayer in a prescribed format, which is then authenticated and validated by the GSTN (Goods and Services Tax Network). The e-invoice contains a unique invoice reference number (IRN), which is generated by the GSTN, along with a QR code that contains key invoice details.
Easy Process and Documentation
Required Paperwork
- GSTIN
- Invoice details
- IRN (Invoice Reference Number)
- QR code
- Digital signature
- Supporting documents-purchase orders,
delivery challans, and payment receipts - E-way bill
Process, Service Charges, Time duration
- When you send us your paperwork, our experienced staff will review your paperwork with local government officials to determine the service’s cost, feasibility, and completion date. After a quote has been given, it remains fixed. Location affects project duration and cost. Send us your documents and specific requirements to get a price and turnaround estimate.
- On an average Procurement takes four to six weeks.
2000+ locations Served
Happy Clients 50000+
Averge Google Rating 4.9
India's Most Trusted Legal Documentation Portal
Since the GST council gave its approval to the idea of e-invoicing, there has been a lot more talk about it in the business world. The GST council approved e-invoicing at its 37th meeting, which took place in September 2019. The main goal was to make sure that e-invoices could be used across the GST eco-system.
Since the invoice is a very important document and e-invoicing is a change to it, it is very important for businesses to fully understand it and get ready for it.
Let’s talk about and figure out everything about e-invoicing under GST in this article.
What is e-invoice in GST?
e-Invoice known as ‘Electronic invoicing’ is a system in which all B2B invoices are electronically uploaded and authenticated by the designated portal.
Post successful authentication, a unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN) is generated for each invoice by IRP. Along with IRN, each invoice is digitally signed and added with a QR code. This process is collectively called e-invoicing under GST
Know more on IRN, Format and process to generate it.
Why e-Invoicing is introduced?
Even though the invoices made by each software look pretty much the same, the computer system can’t understand them. Business users, on the other hand, can fully understand them. For example, a machine running “B” accounting software can’t read an invoice made by “A” accounting software.
There are hundreds of accounting and billing programmes that can make invoices today, and each one has its own way of storing information. The GST system can’t read and understand these invoices because of this, even though the information on them stays the same.
To make a long story short, the same information is now shown in different ways on different invoices, making it impossible for a system to understand it.
What are the pros of an electronic invoice?
The main reason for using e-invoices is to fill out the returns ahead of time and make them easier to match up. This is made possible by how the IRP system is set up. It shares invoice information with the GST system and the e-way bill system. So, if you keep uploading invoices, most of the information you need for returns and the e-way bill will be filled in automatically.
The following are some of the key benefits of e-invoicing:
- Reduces reporting of same invoice details multiple times in different forms. It’s just a one-time upload and everything, as required, will get pre-populated.
- Part-A of e-Way bill will be auto-captured and only transporter details are required to be updated.
- On uploading of invoices, the B2B details will be auto-captured in GSTR-1 return.
- Substantial reduction in input credit verification challenges as the same data will get reported to the tax department as well to the buyer in his inward supply (purchase) register (GSTR-2A).
- On receipt of info from the GST System, a buyer can do a reconciliation with his Purchase register and accept/reject it on time under New Return.
- A complete trail of B2B invoices and system-level matching of input credit and output tax helps to reduce tax evasion
- Increase efficiency in tax administration by eliminating fake invoices.
How will e-invoicing curb tax evasion?
E-invoicing has a lot of benefits, and one of them is that it can help stop tax evasion. With an e-invoice, it will be hard to change the bill because the bill is made before any transaction takes place. E-invoices are also helpful because they make sure that the government knows about all transactions in real time. Due to automation and thorough checks, e-invoicing cuts down on fake GST invoices by a lot and makes sure that input tax credit is claimed on real GST invoices. If someone tries to get a fake tax credit, GSTN can find them easily.
What are the mandatory fields of an e-invoice?
The following are the 30 mandatory fields of an e-invoice. Earlier, 50 fields were to be mandatorily filled by the taxpayer.
Field name | Description |
Document Type Code | Every type of document has a code and this must be specified in this portion. |
Supplier Legal Name | The name of the supplier according to the PAN card details. |
Supplier GSTIN | The supplier GSTIN for e-invoice. |
Supplier Address | The full address of the supplier including flat number, building no. etc. |
Supplier Place | The city/village/town of the supplier must be specified here. |
Supplier State Code | The state must be selected. |
Supplier Pincode | The six-digit pin code of the supplier’s address. |
Document Number | A unique invoice number that makes sense to the business. It has to be sequential for easy identification. |
Preceding Invoice Reference and Date | The original invoice details are being edited using a document such as a credit note. |
Document Date | The date on which the invoice was issued. |
Recipient Legal Name | The name of the buyer is specified as per his PAN card. |
Recipient’s GSTIN | The buyer’s GSTIN needs to be specified. |
Recipient’s Address | The detailed address of the buyer has to be specified. |
Recipient’s State Code | The place of supply has to be specified. |
Place of Supply State Code | The state of the recipient has to be selected. |
Pincode | The location of the recipient has to be selected. |
Recipient Place | The village/town/city of the recipient has to be specified. |
Invoice Reference Number or IRN | The supplier leaves the field empty at the time of registration and after that GSTIN generates a unique number when the e-invoice is uploaded on the GSTN portal. As the e-invoice is accepted, acknowledgment is sent. Before the use of an e-invoice, the IRN has to be displayed on it. |
Shipping To GSTIN | GSTIN of the person the item is being delivered to. |
Shipping To State, Pincode and State Code | This field specifies the place where the goods and services are delivered. |
Dispatch From Name, Address, Place and Pincode | The name of the dispatching entity along with the city/town/village specifics. |
Is Service | If supply of service has to be specified. |
Supply Type Code | The type of supply and its responding code is specified. It can be supply to SEZ, B2B, etc. |
Item Description | The item’s description. |
HSN Code | The particular code for the goods or services. |
Item Price | The GST exclusive unit price prior to the item price discount being subtracted. This value must be positive. |
Assessable Value | The item’s price excluding GST and after the item price discount has been subtracted. |
GST Rate | The rate of the specific item for which the invoice has been generated. |
IGST Value, CGST Value and SGST Value Separately | Every item must have IGST, SGST, and CGST. |
Total Invoice Value | The total value including GST. |
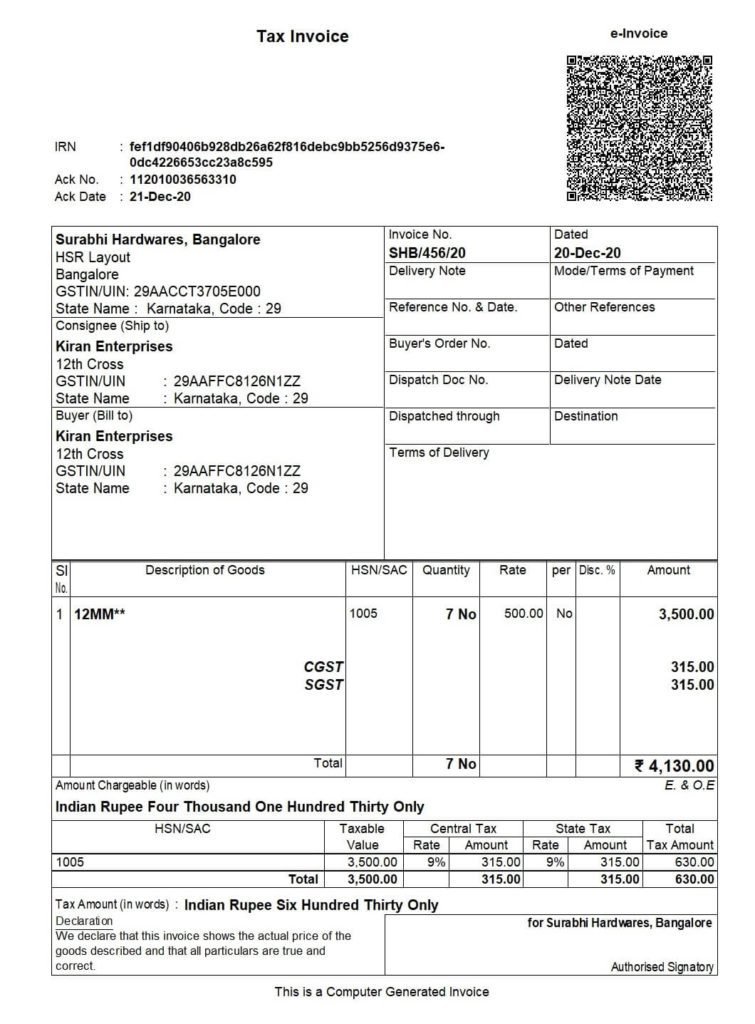
What does the e-invoice look like?
All businesses must use the e-invoice format that is shared by the GSTN. The e-invoice must have all of the fields, both the required ones and the ones that aren’t. All taxpayers have to fill out the fields that say they have to. When it makes sense, the taxpayer has to fill out the fields that aren’t required. This is what an e-invoice looks like.
When will e-invoicing be introduced?
To ensure that businesses get enough time to adapt to the new system of electronic invoicing, the GST Council has approved the introduction of e-invoicing in a phased manner.
Annual turnover | New date of mandatory implementation of e-invoice |
Exceeding 500 crore | 1st October, 2020 |
Exceeding 100 crore | 1st January,2021 |
Exceeding 50 crore | 1st April,2021 |
Exceeding 20 crore | 1st April,2022 |
Exceeding 10 crore | 1st October, 2022 |
In the recent update, e-invoicing will be applicable for businesses with a turnover exceeding 10 crores from 1st October 2022.
Type of business to whom e-invoice will be applicable?
Electronic Invoicing will be applicable to all the businesses that are registered under GST and issuing B2B invoices in phased manner as discussed above.
Who need not comply with e-Invoicing?
According to the latest rule, all businesses with a turnover of more than 10 crores will have to start sending e-invoices on October 1, 2022. As of right now, businesses with less than the required amount of sales don’t have to follow the e-invoicing rule. But as of January 1, 2023, businesses with an annual revenue of Rs. 5 crore or more will also have to send e-invoices.
What is the system in place for issuing invoices before e-invoicing?
Businesses could send invoices using any third-party software they wanted at the time. The business then had to enter the invoice details by hand into the GSTR-1 return. When this was done correctly, the information entered showed up on the GSTR-2A form by itself. This form can only be looked at. For e-way bills to be made, the transporters had to manually import the invoices.
Who should upload the e-invoice?
Under the idea of e-invoice, the seller must electronically upload the invoice to the IRP system and include the QR code and IRN (Invoice Reference Number) on the copy of the invoice that is sent to the recipient.
What type of documents are to be reported to GST system?
The following documents are covered under the concept of e-invoice. Meaning the creator of these document needs to upload it to the IRP system.
- Invoice by Supplier
- Credit Note by Supplier
- Debit Note by Supplier
- Any other document as required by law to be reported by the creator of the document
How is e-invoice different from the current practice of invoicing?
E-invoice is a system in which the bill must be uploaded electronically and verified with a unique invoice reference number (IRN) and digitally signed QR code. The change is that the seller now has to print the QR code and IRN number on the invoice before giving it to the buyer.
Businesses that use ERP or business management software that connects easily to the IRP system and automatically prints the QR code and IRN on the invoice will find it easy to meet e-invoice requirements without making many changes to how they do business.
What are the modes of generating e-Invoice?
Multiple modes will be made available so that the taxpayer can use the best mode based on his/her need. The following are different modes of generating e-Invoice?
- Web-Based,
- API Based,
- SMS Based,
- Mobile App
- offline tool based and
- GSP based
PARTNERSHIP FIRM REGISTRATION FAQS
You cannot cancel an e-invoice partially. If you want to cancel the e-invoice, you have to do it all the way. When you do this, you must tell the IRN within 24 hours of the cancellation. If you try to cancel an e-invoice after that time, you can’t use the IRN. For cancellation, you need to use the GST portal, and you have to do it by hand. This has to be done before the taxes are turned in. When you cancel, you can’t use the same invoice number again. Instead, you have to make a new one, or the IRP will turn it down.
e-Invoicing has two parts: the first is the interaction between the business and the IRP, and the second is the interaction between the IRP, the GST/E-Way Bill Systems, and the buyer.
E-invoicing makes it easier for businesses to send invoices, which cuts down on paperwork and shortens the time it takes to process invoices.













